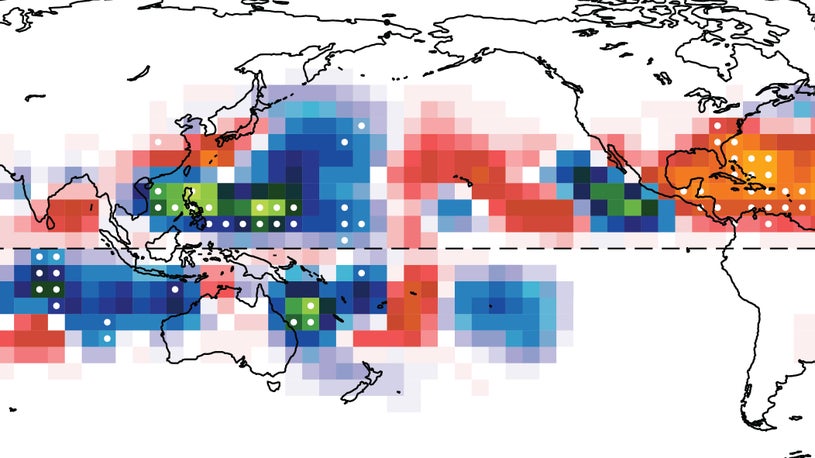
- Tropical cyclone frequency has increased since 1980 in the North Atlantic and Central Pacific oceans.
- The frequency of storms has decreased in the western Pacific and southern Indian oceans.
- Climate change is at least partially to blame.
Climate change has altered how frequently tropical cyclones form in the world's oceans over the past 40 years, according to a new study led by NOAA.
A tropical cyclone is a low pressure system with an organized circulation and concentrated shower and thunderstorm activity. They are commonly called hurricanes, cyclones, typhoons, tropical storms and depressions, depending on the ocean in which they are located.
The study found that the frequency of tropical cyclones increased in the North Atlantic and Central Pacific ocean basins in the years from 1980 to 2018. Tropical cyclones also increased in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal in the northern Indian Ocean. You can see this in the red and orange shadings in the map below.
Orange and red shaded areas saw an increase in the frequency of tropical cyclones from 1980-2018. Blue and green shaded ocean areas had a decrease in tropical cyclone frequency.
(NOAA)Conversely, areas shaded blue and green had a drop in the frequency of tropical cyclones, including large areas of the northwest Pacific and southern Indian oceans. The southwest Pacific Ocean to the northeast of Australia and the far northeastern Pacific Ocean, or off the west coast of Mexico, also saw decreases.
The study found that natural variability in the world's climate doesn't fully explain the observed changes in the past 40 years. Increasing greenhouse gases, less pollution and volcanic eruptions were cited as factors.
Warming ocean water, which is a key ingredient that tropical cyclones need in order to form, is one reason for the pronounced increase in the frequency of tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic. That's because there has been a decrease in pollution from particles and aerosols, resulting in less cloud cover and more sunlight heating the oceans.
Rising greenhouse gases have also contributed to an overall warming of the earth, including the oceans.
Volcanic eruptions caused temporary changes in tropical cyclone frequency from 1980 to 2018, the study added.
Eruptions from El Chichón in Mexico in 1982 and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991 caused tropical cyclone activity in the Northern Hemisphere to shift southward. The emissions from those volcanoes cooled the atmosphere and resulted in less heat reaching the oceans. However, that influence ended by 2000, leading to an increase in tropical activity in the Northern Hemisphere.
What About the Future?
Continued increases in greenhouse gases could eventually lead to a decrease in the total number of tropical cyclones worldwide in the future. That's because warming of the upper atmosphere and oceans is expected to make conditions more stable and therefore less hospitable for the formation of the convection (showers and storms) needed to form tropical cyclones.
The average number of tropical cyclones worldwide per year has been 86 over the past four decades. That number is expected to decline to around 69 annually by the end of the 21st century. This decrease is across most of the world's ocean basins, including the Atlantic. The Central Pacific, which includes the waters around Hawaii, is the only location where a long-term increase in the number of tropical cyclones is anticipated.
Despite the overall global decrease in numbers, tropical cyclones are expected to become more severe in the future because of warming and rising oceans.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
"occur" - Google News
May 07, 2020 at 01:09AM
https://ift.tt/2L88Cm4
Climate Change Has Altered Where Tropical Cyclones Occur Most Frequently, Study Says - The Weather Channel
"occur" - Google News
https://ift.tt/2UoDqVw
https://ift.tt/2Wq6qvt
Bagikan Berita Ini















0 Response to "Climate Change Has Altered Where Tropical Cyclones Occur Most Frequently, Study Says - The Weather Channel"
Post a Comment